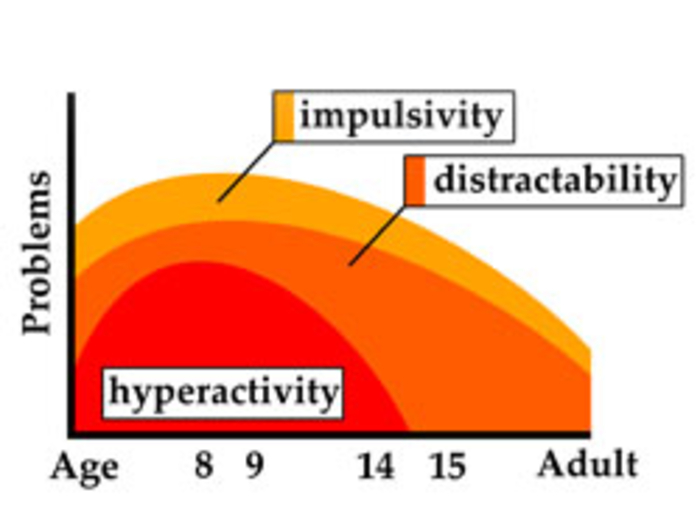
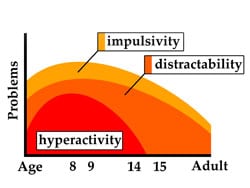
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a developmental condition of inattention and distractibility, with or without accompanying hyperactivity. An estimated 15%-20% of children with ADHD maintain the diagnosis into adulthood, and as many as 65% of these children have ADHD or residual symptoms as adults. Do you know the signs and symptoms to look for and best treatment practices? Test yourself with this quick quiz.
The specific criteria for diagnosis require at least six symptoms of inattention or hyperactivity-impulsivity (or both) that have persisted for at least 6 months. In addition, ADHD is specified by the severity based on social or occupational functional impairment: mild (minor impairment), moderate (impairment between "mild" and "severe"), or severe (symptoms in excess of those required to meet diagnosis; marked impairment).
Brain imaging, such as functional MRI or SPECT scans, has been useful for research, but no clinical indication exists for these procedures because the diagnosis is clinical.